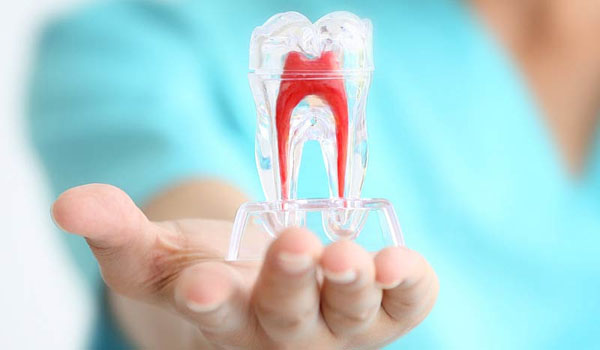
An element of a tooth’s root canal, as opposed to a treatment, is called the “root canal.” The pulp, commonly referred to as the hollow part of a tooth, is where the nerves, arteries, and other tissues are located.
The crown and roots make up a tooth. The sources are below the gum, whereas the height is above it. The pulp supplies nutrition and moisturises the tooth’s surrounding tissue. The nerves in the pulp perceive heat and cold as being unpleasant.
3 steps can make up this root canal therapy; here you can check this out:
- Root canal washing
While the patient is under local anaesthesia, the dentist makes a tiny access gap on the tooth’s surface and uses tiny files to erase the damaged and dying pulp tissue.
- Completing this root canal
A dentist utilizes the irrigation treatment and small files to clean, disinfect, and provide a proper shape to the hollow area. After that, a foam substance is used to fill the tooth, and adhesive cement is utilized to close those root canals fully.
Everyone should take proper care of their teeth. Even after getting root canal therapy, the tooth is still dead. The patient won’t feel any pain in her tooth anymore because the infection and nerve tissue have been erased.
- Crowning or filling a tooth
The tooth without any pulp must also be fed by a ligament that holds it to the bone. Even while there is enough, your tooth will gradually grow more delicate. Thus, that crown or the filling offers security.
Till the crown is complete, the patient shouldn’t also bite down on or chew on the tooth. After a crown has been kept, a person can utilise the tooth typically.
But When there are bent canals, multiple tunnels, or serious infections, therapy can necessitate further appointments. For getting to the root of the treatment, you can take some painkillers for the primary stage with the help of your dentist.
Advantages of the root canal surgery
The first step of a completely painless operation known as the root canal is the removal of unhealthy or damaged pulp from the root cavity. A typical polymer material used in root canal treatment, gutta-percha, is then utilised to fill the cavity once it has been cleaned and sanitised.
What advantages make root canal patients’ and endodontists’ preferred procedures? Here are a few benefits:
It prevents tooth loss, avoids infection of nearby teeth, improves the appearance of teeth, stops jawbone deterioration, and improves oral and general health. To get the best treatment in this field, you have to choose the best place that can give you the best solution for every teeth problem. For this treatment, you should choose the best procedural dentist.
Conclusion
A necessary treatment for cavities and tooth decay is a root canal. It prevents tooth loss and is essentially painless. In addition to improving oral and general health, root canal therapy also protects neighbouring teeth from infection and preserves the aesthetic appeal of teeth.